Agile software development has gotten more and more attention in the last couple of years. Not only internet startups or media agencies but also large companies from conservative business lines like automotive, banking, insurance, and the public sector are more and more adjusting to the agile world.
Since those companies are often already very much security-aware, at least from a governance perspective, the question of how to ensure the security of applications that are developed in such a way has been asked more and more frequently in the last time.
First of all, agility is not bad for security! It is, however, in fact, challenging. It can in fact be quite positive for security. This, however, often requires not less than a mind change. Not only in development but also in security as well. The latter often just don’t understand how Agile security and DevOps actually work, which is of course essential when you want to secure it.
So let’s have a look at what agile development is in respect of security very quickly: Agile development means that you have product iterations instead of a linear process. These iterations are often two or four weeks long and end up in some sort of testable artifact. It does, however, not mean that you have a release in production every two or four weeks.
In fact, you can have an agile development project that works on two weeks sprints but just pushed two releases in production each year. On the other hand, we have DevOps which is based on methods like Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment that can lead to numerous changes in production each day.
This is an important aspect from a security point of view: If a team is working agile but just releases let’s say two in a year, we can of course easily implement a security sign-off (aka final security reviews) in form of a pentest before each release. In a DevOps world, however, this will clearly not be an option.
Secure (Test) Automation
The more Continuous or DevOps you are working (= the more frequently you push releases into production) the more you need to automate security. This does not necessarily mean test automation, although this is of course an important aspect.
Security test automation often means that we run certain code scanning tools (SAST) or website scanning tools (DAST) within the build chain to ensure security. Nowadays a large number of commercial and OpenSource tools exist that we can automatically execute as part of a building job from within a continuous integration server such as Jenkins. Since at least OpenSource tools are often very much focused on specific languages or problems, we usually have to combine a number of them to test an enterprise application. This is what we call AppSec Pipelines.
Sounds great, is however often quite difficult to implement, especially if you want to apply them to complex applications and/or a couple of agile teams at once. Also, if you have DevOps teams they may not be delighted to have a special pipeline that runs for 30+ minutes only for security scans when the usual requirement for a complete build chain is 5-10 minutes.
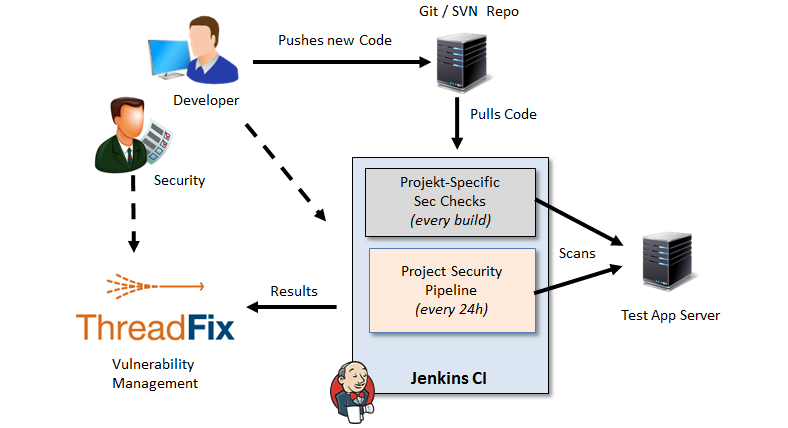
At least this point can be improved by setting up a dedicated security pipeline that runs once a day whereas small and smart security tests are defined that are allowed to be executed within the regular build chain.
IAST solutions can help here, since they are not executed within the build itself but scan the application passively as it is tested by regular integration tests. Such solutions are, however, not cheap and therefore not an option for everyone.
Secure Foundation
When you work a lot with security test automation like I do you realize that this cannot be the solution for security, especially not in Agile teams with or without DevOps. It’s an important pillar, nothing more. Tools need to be configured a lot, they need to be operated by someone, and they will through false positives and a lot of false negatives (vulnerabilities that have not been identified).
If you want to solve this problem, you need to think about how you can prevent vulnerabilities from being introduced in the application code in the first place. This can be accomplished with smart technology choices (e.g. secure frameworks), strict coding principles, secure defaults, and a security architecture that enforces as much security as possible. This is actually what we need to spend more time thinking about. Agile security will not primarily be solved by testing but by engineering!
You will realize that with a solid secure foundation implemented, you will not have to test for everything anymore. Instead, you can now focus on smart tests that cover those spots not covered by your secure foundation, for example insufficiently implemented access controls. Such security tests are usually fast and can normally be executed with very little or no false-positive behavior at all with every build.
Team Responsibilities & Agile Security Practices
Last, but not least important, agile security is not a problem that we can solve with technology alone. It needs to be understood as the responsibility of the team itself. Agile security is a lot about shifting responsibilities into the development team (e.g. tests, operation, …), security needs to be one of them!
Furthermore, security needs to be “legalized”, which means security activities need to be planned by the project manager and must be a part of each sprint planning and retrospective. Instead of executing a full-fledged pentest, we can specify that a new functionality needs to be pentested and create a sub-task for this. Such security-relevant stories can be again collected and handled within one dedicated “security” sprint so that we do not need to onboard a pentester for each sprint.

What has to be done within a sprint from a security perspective (e.g. executing a SAST scan and assessing the results) can be defined in the Definition of Done (DoD). Security User stories can be created and get story points and many more.
Conclusion
As mentioned above, agile and security are not mutually exclusive. In fact, it’s quite the opposite: Agile practices can influence product security very positively. This however often requires a lot of work, technology, and often nothing less than a mind change, not only within the development. Agile development needs to be understood by the security function as well. And, most importantly, security needs to be accepted by the agile dev teams as their responsibility.
